[10000印刷√] model of dna structure and replication 143083-Dna structure and replication model 1
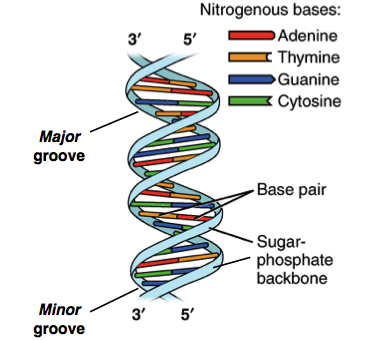
Double Helix Model developed by Watson and Crick DNA molecule made up of 2 connected chains of nucleotides forming a ladderlike structure Side of ladder are made of alternating phosphate and deoxyribose molecules Rung of ladder made up of pair of · DNA Replication Types of DNA replication Semiconservative model of DNA replication Prokaryotic DNA replication Eukaryotic DNA replication Inhibitors of DNA replication (Analogues, Intercalation, Polymerase Inhibitors) DNA damage Types and agents of mutations Spontaneous, Radiation, Chemicals Repair mechanisms Base Excision, Nucleotide Excision, Mismatch Repair DNADownload File PDF Pogil Dna Structure And Replication Answers Imagine that we had some way to look directly at the molecules in a living organism An xray microscope would do the trick, or since we're dreaming, perhaps an Asimovstyle nanosubmarine (unfortunately, neither is currently feasible) Think of the wonders we could witness

Models Of Dna Structures Babyhabsbio11
Dna structure and replication model 1
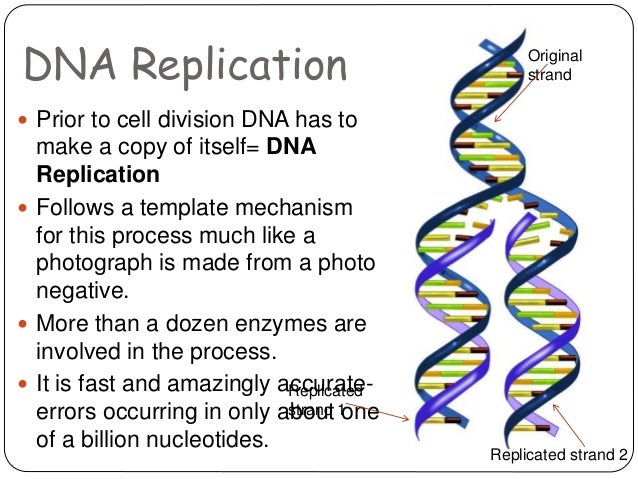
Dna structure and replication model 1-The purpose of DNA replication is to create two daughter DNA molecules which are identical to the parent molecule DNA Replication is SemiConservative Watson and Crick model suggested that DNA replication is semiconservative It implies that half of the DNA is conserved · Mechanism of Replication of DNA suggested by Watson and Crick The two strands of DNA would separate and act as a template for the synthesis of new complementary strands After the completion of replication, each DNA molecule would have one parental and one newly synthesised strand This scheme was termed as semiconservative replication of DNA




Bioknowledgy 7 1 Dna Structure And Replication Ahl
DNA is the molecule of heredity It contains the genetic blueprint for life For organisms to grow and repair damaged cells, each cell must be capable of accurately copying itself So how does the structure of DNA allow it to copy itself so accurately that cells can then replicate during cell division?Scientist Rosalind Franklin discovered (b) the Xray diffraction pattern of DNA, which helped to elucidate its double helix structure (credit a modification of work by Marjorie McCarty, Public Library of Science) Watson and Crick proposed that DNA is made up of two strands that are twisted around each other to form a righthanded helixTherefore, a tissue category does not apply The
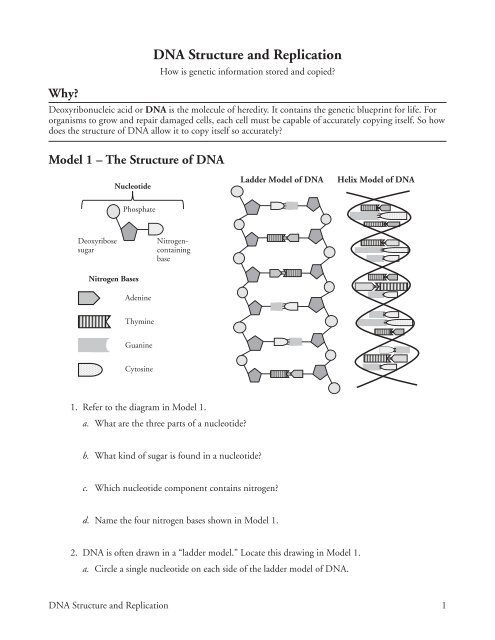
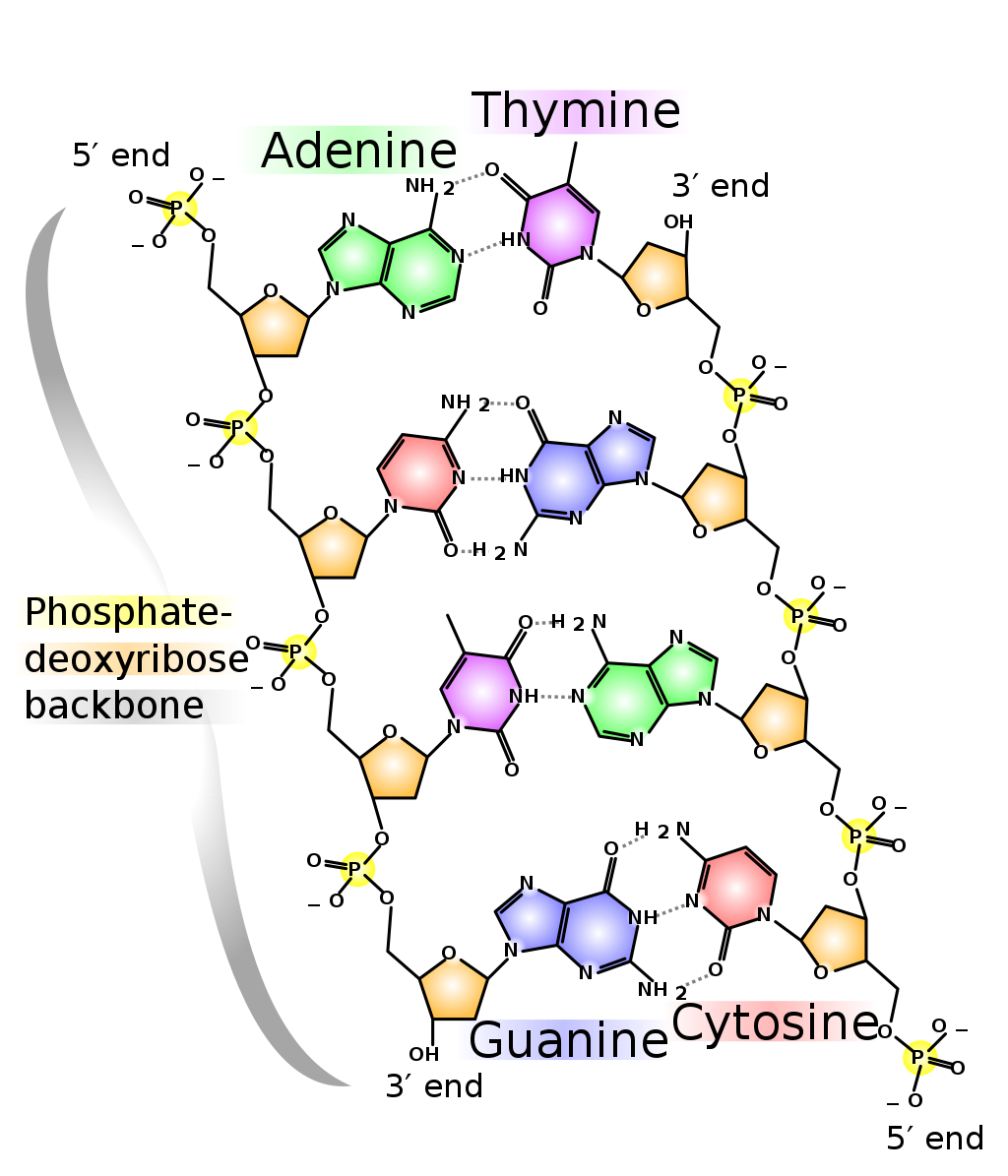
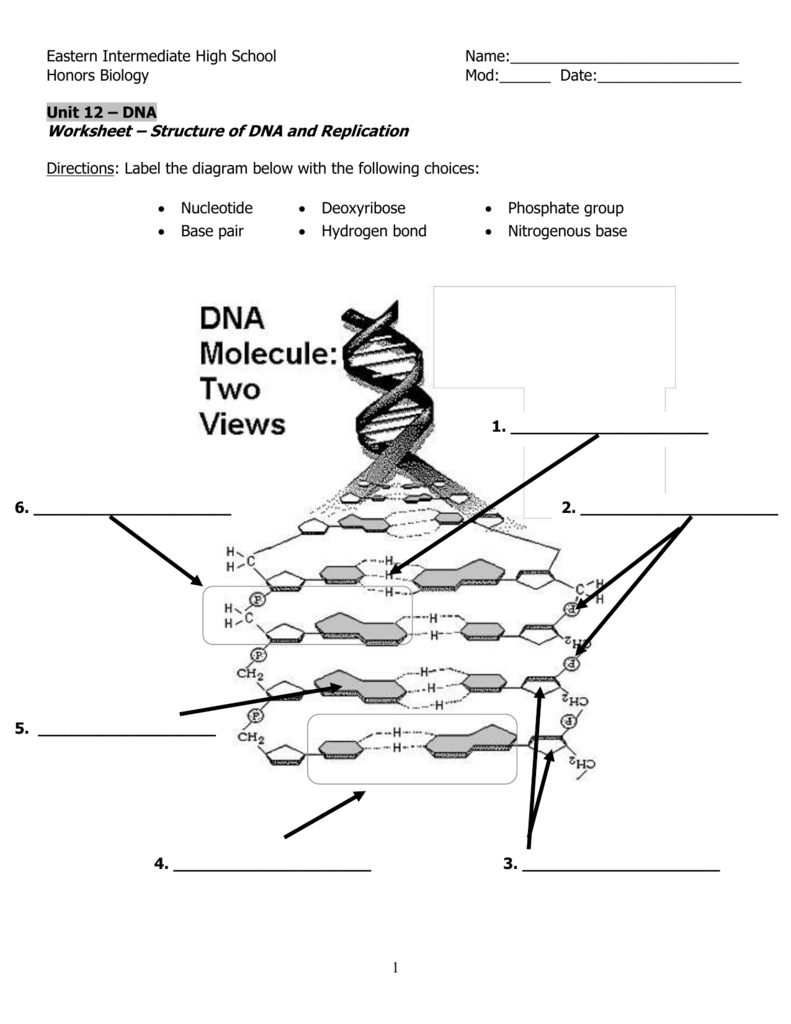
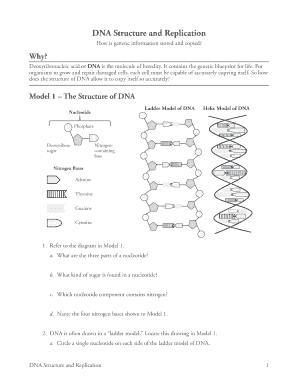
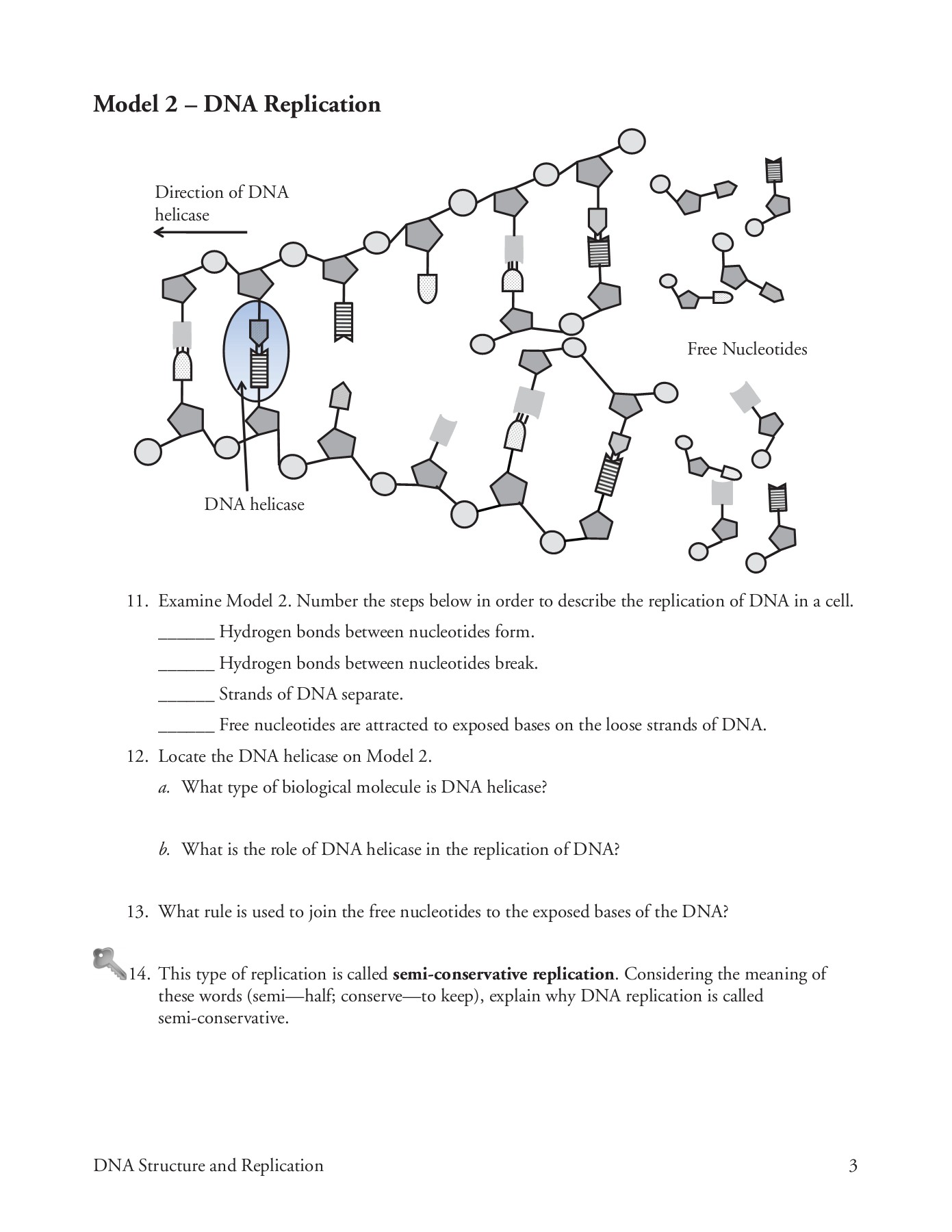
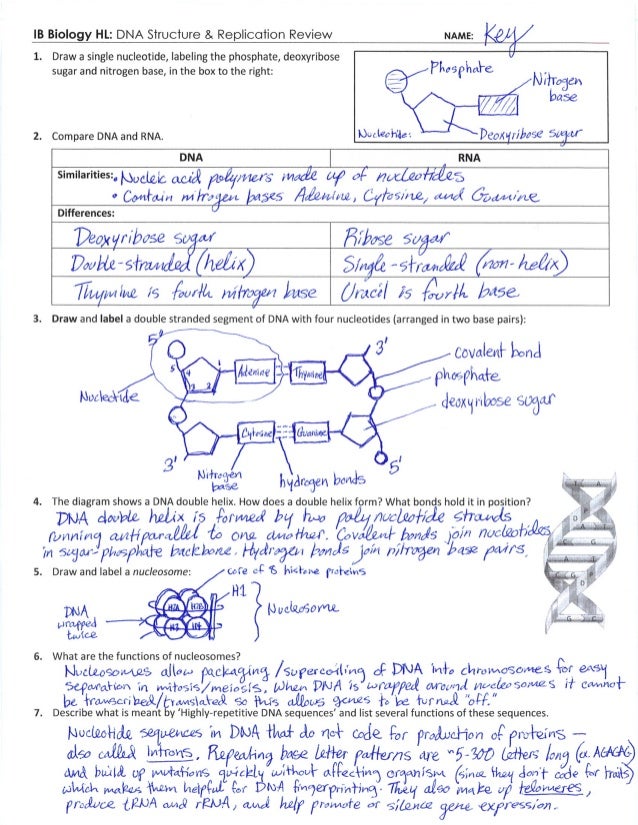
· The replication is a process in which a DNA molecule becomes doubled through the enzymatic reactions Watson and Crick model of DNA The molecular structure of DNA was proposed by Watson and Crick in 1953 Their findings were based on previous discoveries Some of the pieces of evidence are given below, Evidence DNA is the genetic material The DNA was firstDNA Structure and Replication 1 DNA Structure and Replication How is genetic information stored and copied?Model 1 – The Structure of DNA Nucleotide Deoxyribose sugar Nitrogencontaining base Nitrogen Bases Adenine Thymine Guanine Cytosine 1 Refer to the diagram in Model 1 a What are the three parts of a nucleotide?
In this review, we summarize recent findings and current models linking spatial and temporal regulation of the replication program with epigenetic signaling We discuss these issues in the context of the genome's threedimensional structure with an emphasis on events occurring during the initiation of DNA replicationDNA Structure and Replication Home DNA Experiments The Double Helix Semiconservative Model Enzymes/AntiParallel DNA Repair Test Your Knowledge About History of the Semiconservative Model How it Works The semiconservative model was introduced and proven in 1957 through an experiment conducted by Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl MeselsonA replication unit is any chunk of DNA that is capable of being replicated — eg a plasmid with an origin of replication (ORI) is a replication unit Alternatively, this can also mean a region of DNA that is replicated together An ORI is a DNA sequence at which replication is initiated
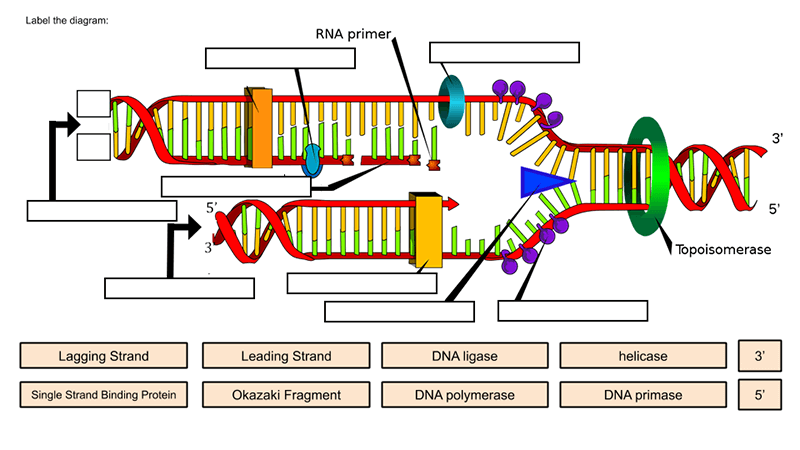



Dna Drag And Drop




Eukaryotic Dna Replication A Model For A Fixed Double Replisome Trends In Genetics
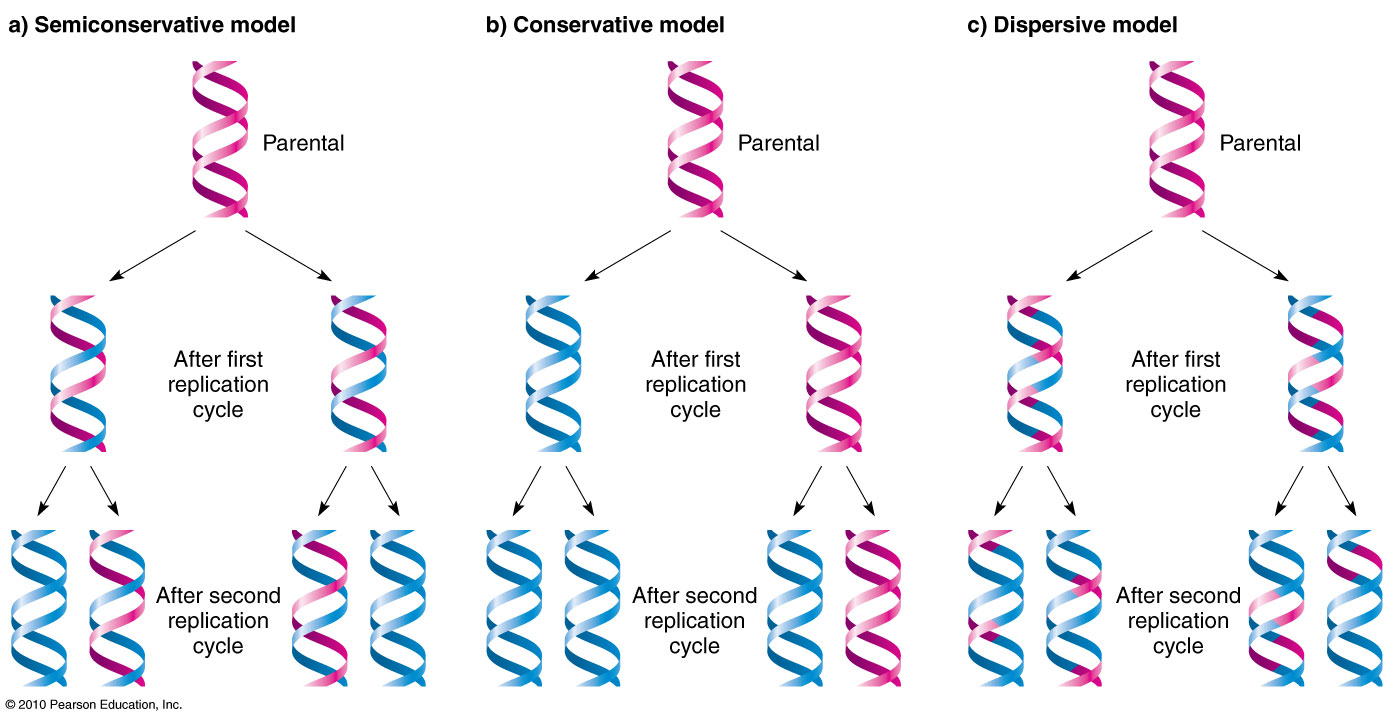
DNA is made up of subunits which scientists called nucleotides Each nucleotide is made up of a sugar, a phosphate and a base There are 4 different bases in a DNA molecule adenine (a purine) cytosine (a pyrimidine) guanine (a purine) thymine (a pyrimidine) The number of purine bases equals the number of pyrimidine basesTranscriptThis is a model of DNA, a double strand of DNA, and when it's replicated, it is replicated semiconservatively So that means that these two stranSemiConservative, Conservative, & Dispersive models of DNA replication In the semiconservative model, the two parental strands separate and each makes a copy of itself After one round of replication, the two daughter molecules each comprises one old and one new strand




Models Of Dna Structures Babyhabsbio11




The Structure Of Dna Genetics The Structure Of Dna
DNA Structure and Replication How is genetic information stored and copied?In coli, the OriC region spans 245•DNA –Only four nucleotides •thought to have monotonous structure •Protein – different amino acids – greater potential




Dna Replication Overview Video Biology Ck 12 Foundation
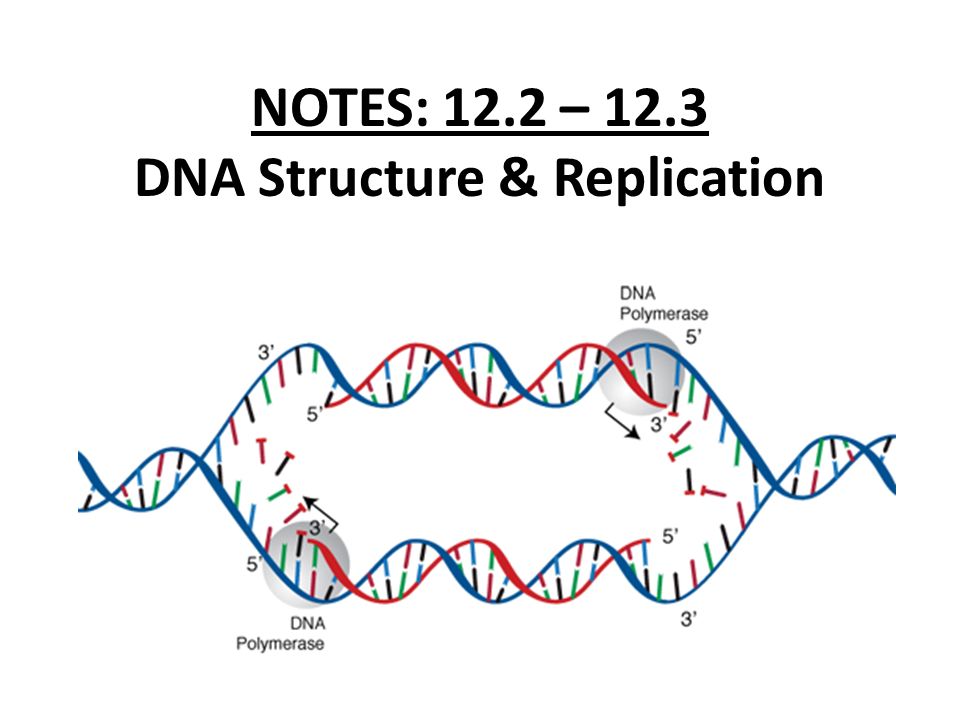



Notes 12 2 12 3 Dna Structure Replication Ppt Video Online Download
Structure and replication of DNA DNA is the molecule that holds the instructions for all living things DNA achieves this feat of storing, coding and transferring biological information though itsFor the last three entries, what is the most likely explanation for the slight differences in the composition of human DNA from the three tissue sources?The fork is generated by a complex of 7 proteins called primasome that includes – Dna G primase, Dna B helicase, Dna C helicase assistant, Dna T, Primase A, B and C;




Heredity Structure And Composition Of Dna Britannica



1
Deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA is the molecule of heredity It contains the genetic blueprint for life For organisms to grow and repair damaged cells, each cell must be capable of accurately copying itself So how does the structure of DNA allow it to copy itself so accurately? · The semiconservative mode of DNA replication was postulated by Watson and Crick along with their doublehelix model of DNA The DNA molecule that undergoes replication may be termed as parent molecule' or 'template molecule', while the two molecules produced by replication may be called progeny molecules' or 'daughter molecules'In their report announcing the structure of the DNA molecule, Watson and Crick observe, "It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material" 1 Some months later, Watson and Crick expanded upon this comment, "our model for deoxyribonucleic acid is, in effect, a pair of templates, each




Dna Replication Wikipedia



Dna Structure And Replication Ramsey School District
Model 1 — The Structure of DNADNA Modeling Molecular Structure & Replication kit #71 This basic introduction to the double helix model of DNA uses simple components developed exclusively by LABAIDS® ♦ Double nitrogen pyrimidine bases are constructed proportionately larger in diameter than the single nitrogen purine bases ♦ Bases are linked by a unique hydrogen bond ♦ The deoxyribose sugar isAnswer The first four are singlecelled organisms;




Dna Replication Microbiology




Dna Replication Steps Diagram Expii
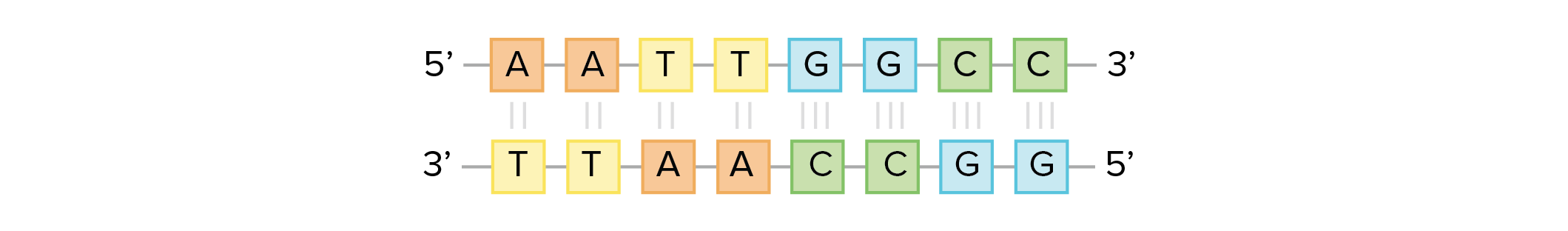
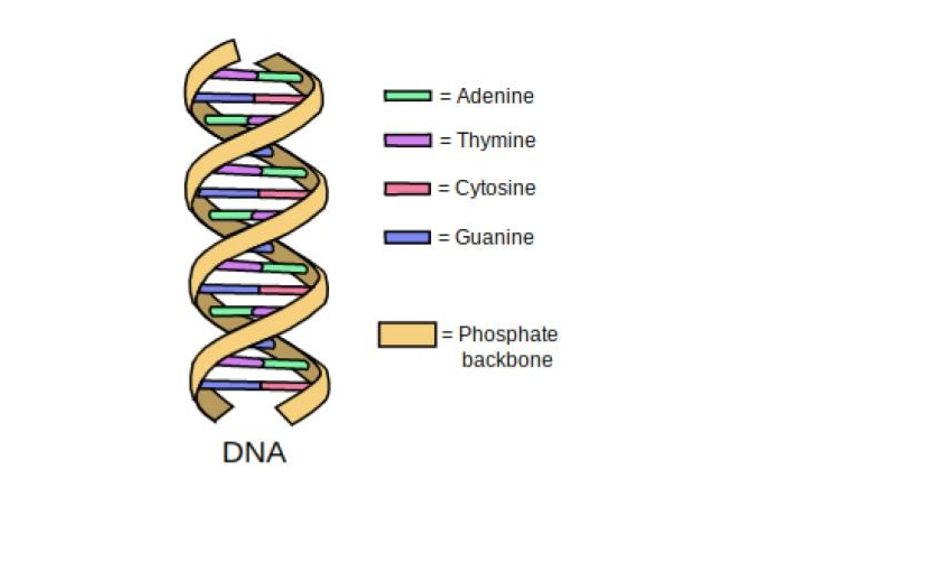
· The structural model of DNA was initially proposed by James Watson and Francis Click They found that DNA is a doublehelical structure with two paired DNA strands with complementary nucleotide sequences The doublestranded DNA molecule has two spiral nucleic acid chains that are twisted into a double helix shapeLadder model of DNA The bases are all always going to be to paired with the base that resembles the base the most Like for example, Adenine will always be paired with Thymine and Cytosine will always be paired with Guamine Fill in the complementary bases on the strand below according to the basepair rule · Send Email Recipient(s) will receive an email with a link to 'A Paper Model of DNA Structure & Replication' and will not need an account to access the content



Dna Structure And Replication




Solved Practice Dna Structure And Replication 1 Label E Chegg Com
Molecular models of DNA structures are representations of the molecular geometry and topology of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) molecules using one of several means, with the aim of simplifying and presenting the essential, physical and chemical, properties of• DNA structure double stranded anti parallel strands • DNA structure helix • Basis for polarity of SS DNA and anti parallel complementary strands of DNA • Models of DNA replication • Mechanism of DNA replication steps and molecular machinery • Fidelity of DNA replication 2 Genetic Material "A genetic material must carry out two jobs duplicate itself and control theDNA Structure & Replication How is the genetic information stored and copied?




7 1 Dna Structure Replication



1
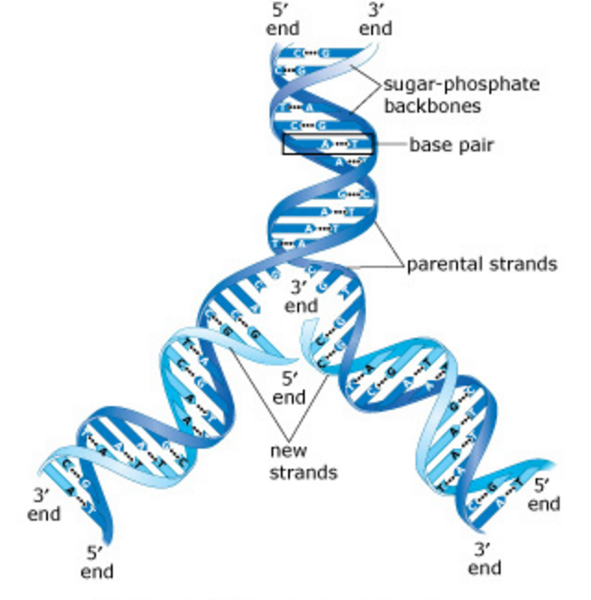
DNA is made up of a double helix of two complementary strands The double helix describes the appearance of a doublestranded DNA which is thus composed of two linear strands that run opposite to each other and twist together to form During replication, these strands are separatedDNA replication is semiconservative Before Watson and Crick model it was believed that DNA molecule undergoes selfduplication or replication, but the exact procedure was not known Watson and Crick's model provided a base for the replication procedure Watson and Crick propose a possible mechanism of DNA replication · Knowledge of DNA's structure helped scientists understand how DNA replicates DNA replication is the process in which DNA is copied It occurs during the synthesis (S) phase of the eukaryotic cell cycle DNA replication begins when an enzyme, DNA helicase, breaks the bonds between complementary bases in DNA (see Figure below)




The Replication Of Dna In Escherichia Coli Pnas




Models Of Dna Structures Babyhabsbio11
· As the DNA unwinds, a yshaped structure is formed at either ends of the replication bubble It is known as the replication fork In such cases, bidirectional replication occurs;Faithful replication of the genetic material (DNA) is the foundation of all life on earth The famous 1958 experiment by Matthew Meselson and Frank Stahl established that DNA replicates through a semiconservative mechanism, as predicted by Watson and Crick, in which each strand of the double helix acts as a template for the synthesis of a new strandStudents will construct a DNA model, describe the structure and function of DNA, sequence the steps involved in DNA replication, and plan and design a model of DNA This lesson should be done after a lesson on the structure and function of cells Learning Outcomes Student will be able to • construct DNA molecules using the 4 nitrogenous bases (ATCG) • write about the structure




Dna Replication Steps Diagram Expii



American Board
Ryn A sugar, a phosphate, and a base DNA Structure and Replication 1Edited version of Paul Anderson's video on DNA structure and replicationThe model for DNA replication is known as the _____ method because half of the parental molecule is maintained, or conserved, in the each daughter molecule origins of replication replication of a DNA molecule begins at particular sites called _____, short stretches of DNA having a specific sequence of nucleotides 3', 5', carbon because the sugarphosphate backbones run in opposite



Dna Structure And Replication Review Article Khan Academy



Dna And Rna Basics Replication Transcription And Translation
View Copy_of_DNA_Structure__Replication_POGIL from ART MISC at Tates Creek High School C G T A 1 Refer to the diagram in Model 1 a What are the three parts of aDNA Structure and Replication WORKING WITH THE FIGURES 1 In Table 71, why are there no entries for the first four tissue sources?To determine the structure of a DNA molecule and to explore how DNA replicates In this lab you will create a 2dimensional model AND a 3dimensional model of DNA



Dna Structure And Replication 5e Lesson By Sunrise Science Tpt




Dna Structure And Replication Diagram Quizlet
Are Genes Composed of DNA or Protein?The doublehelical structure of DNA was introduced to the world by Watson and Crick, and was identified by the use the Xray diffraction techniques to find out the threedimensional structure of DNA Although the globally accepted structure is known as the Watson and Crick model of DNA structure, one important person left out of the historical teaching of DNA's discovery is Rosalind · 11 DNA ReplicationSteps Identification of the origins of replication Unwinding (denaturation) of dsDNA to provide an ssDNA template Formation of the replication fork Initiation of DNA synthesis and elongation Primer removal and ligation of the newly synthesized DNA segments Reconstitution of chromatin structure 12




Genetics Dna Replication And Structure Activity A Hands On Model Dna Dna Model Project Dna Project



Dna Structure And Replication Review Article Khan Academy
Models of the structure of DNA revealed the molecule is made up of two strands of covalently linked nucleotides that are twisted around each other to form a righthanded helix In each strand, nucleotides are covalently joined to two other nucleotides (except at the very ends of a linear strand) via phosphodiester bonds that link the sugars via the 5' and 3' hydroxyl groups (panel bDeoxyribonucleic acid or DNA is the molecule of heredity It contains the genetic blueprint for life For organisms to grow and repair damaged cells, each cell must be capable of accurately copying itself So how does the structure of DNA allow it to copy itself so accurately?DNA Structure and Replication Title DNA Replication Author Robert and Marsha Goodman Last modified by RNA structure, chargaff rule, nucleic acids, ATP, watson and crick model, types of DNA A DNA, B DNA Z DNA, types og rna PowerPoint PPT presentation free to view DNA Replication and Repair Chapter DNA Replication and Repair Replication is bidirectional E
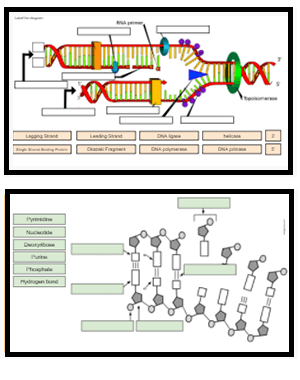



Dna Drag And Drop
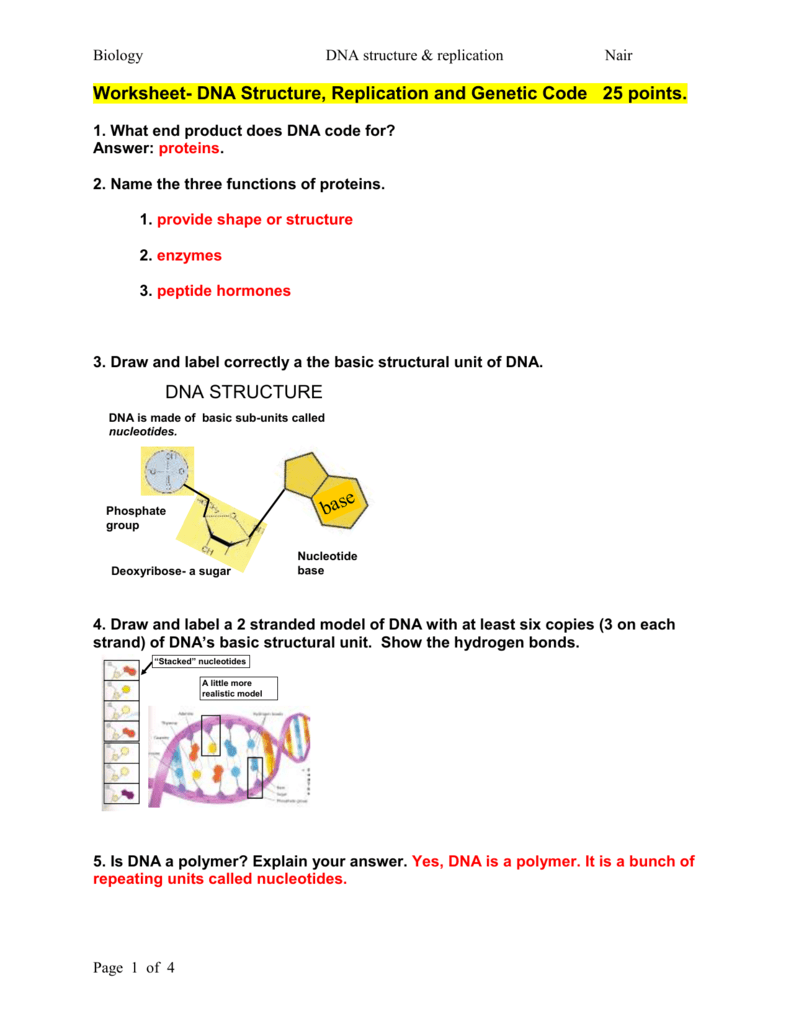



Worksheet Dna Structure Replication And Genetic Code
We already have an overview video of DNA and I encourage you to watch that first but what I want to do in this video is dig a little bit deeper actually get into the molecular structure of DNA and just as a starting point let's just remind ourselves what DNA stands for all right the different parts of the word in different colors so it stands for deoxy deoxyribonucleic ribonucleic ribonucleic



Dna Structure And Replication Worksheet Promotiontablecovers




The Structure Of Dna Genetics The Structure Of Dna




Watson Crick Structure Of Dna




Basics Of Dna Replication Biology For Majors I



Dna Structure And Replication Presentation Biology
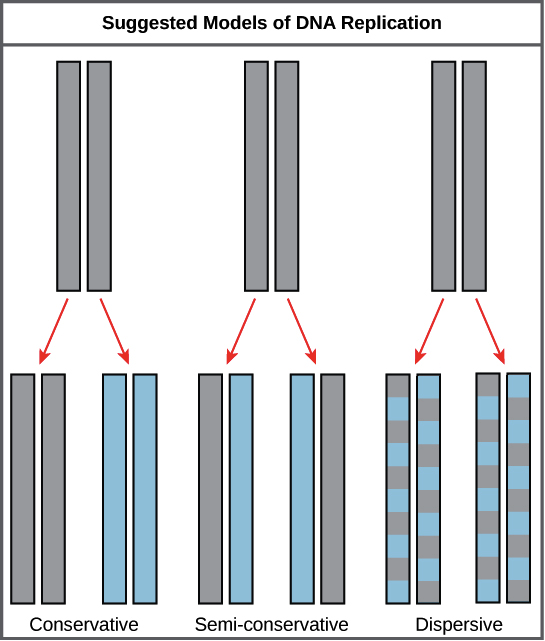



Mode Of Dna Replication Meselson Stahl Experiment Article Khan Academy
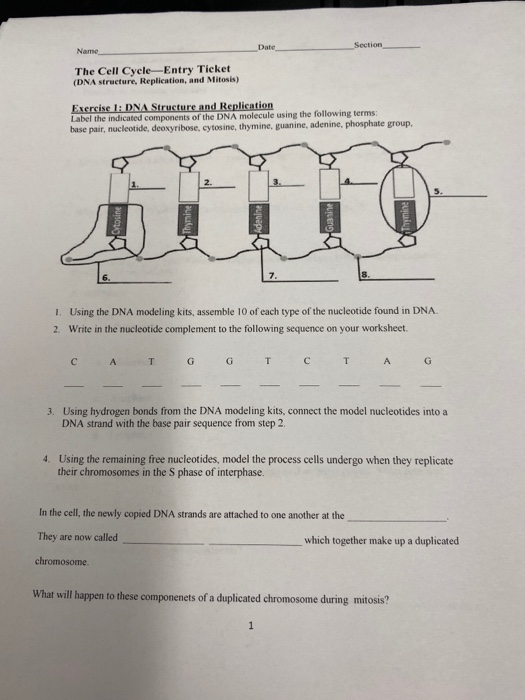



Solved Date Section Name The Cell Cycle Entry Ticket Dna Chegg Com




Make A Candy Dna Model Stem Activity
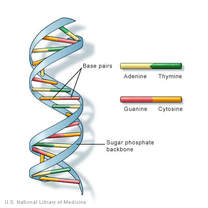



Topic 7 1 Dna Structure And Replication Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green




Dna Structure And Replication Figure 16 5 The Double Helix Ppt Download
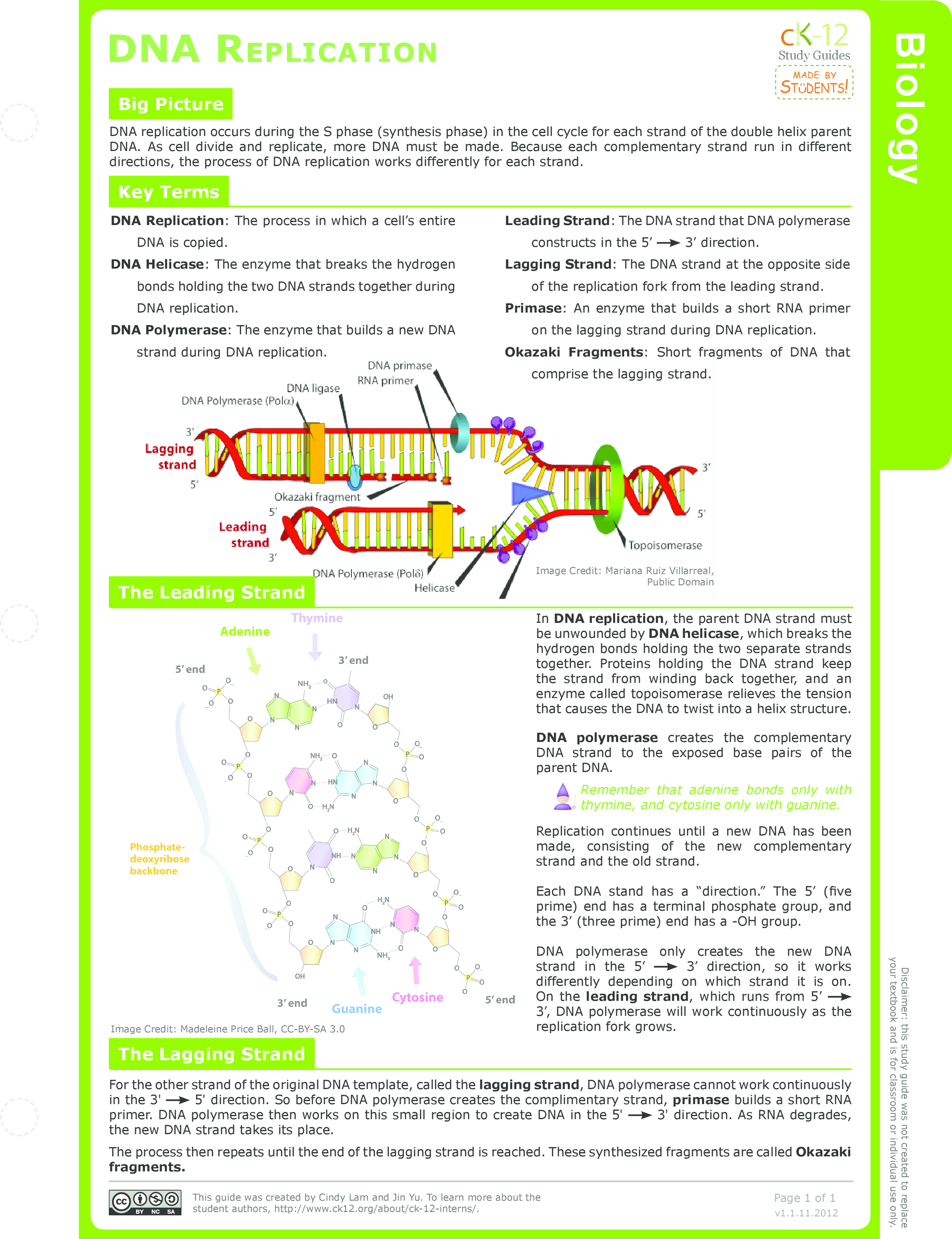



Dna Structure And Replication Ck 12 Foundation




Carbon And Life Biol110f12 Confluence Dna Project Dna Model Project Dna Model
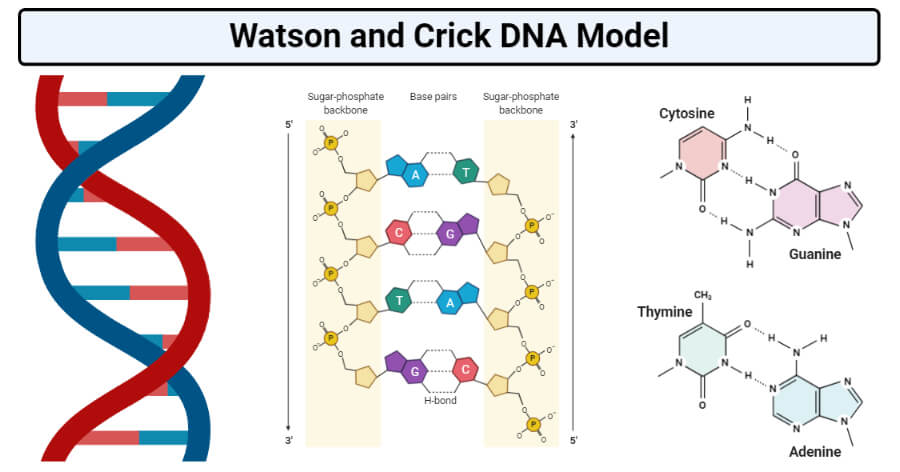



Watson And Crick Dna Model Molecular Biology Microbe Notes
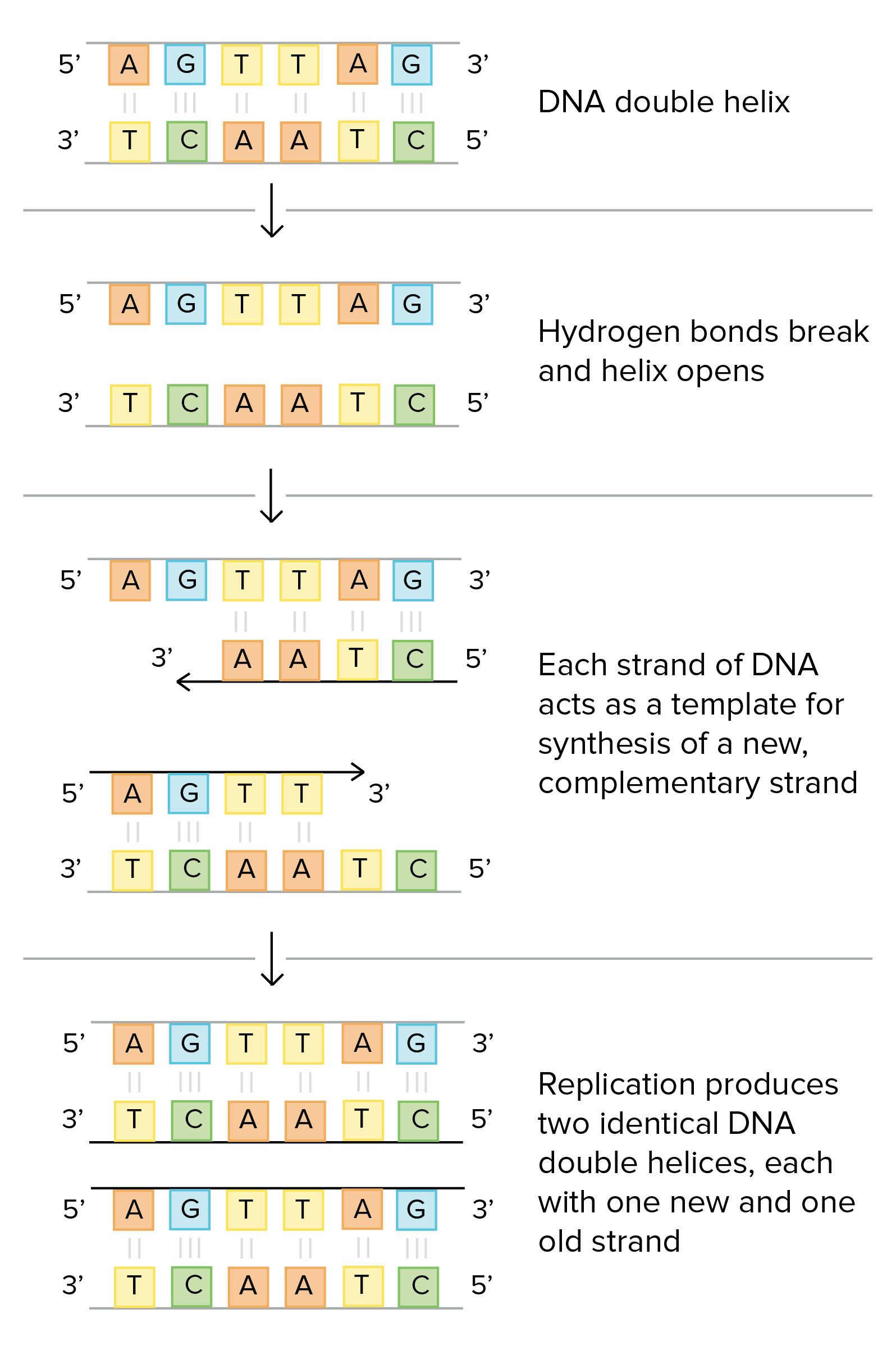



Dna Structure And Replication Review Article Khan Academy




A Paper Model Of Dna Structure Amp Replication Dna Activities Free Science Worksheets Relationship Worksheets



Dna And Molecular Genetics




Dna Replication Structure Stages Of Replication Teachmephyiology
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/nucleotides-5c253d8cc9e77c0001d9b089.jpg)



Dna Definition Shape Replication And Mutation
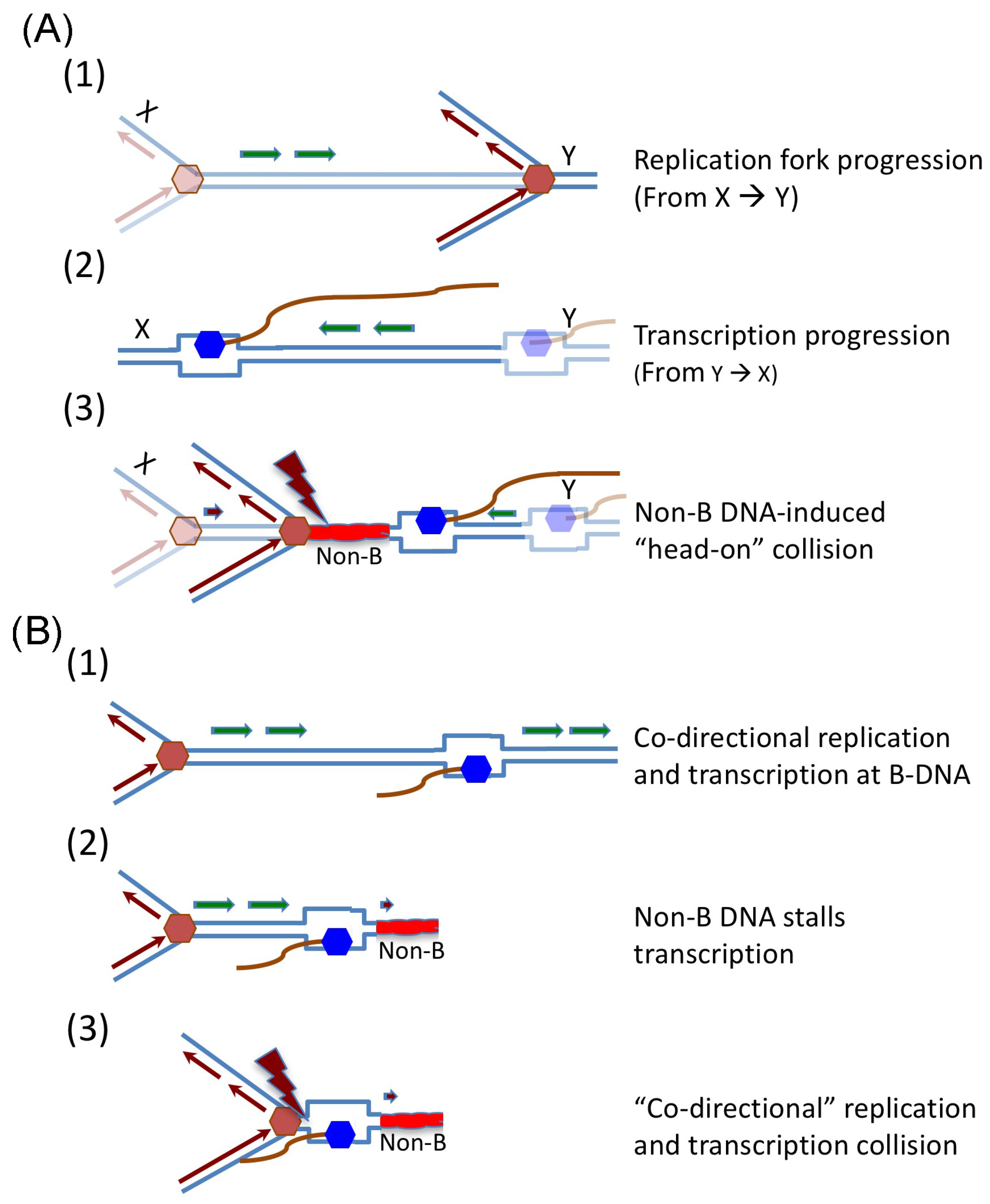



Genes Free Full Text Effects Of Replication And Transcription On Dna Structure Related Genetic Instability Html



1
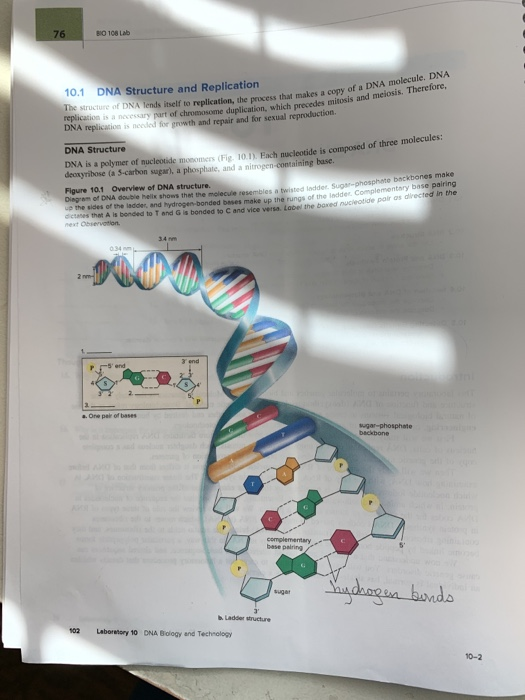



Solved 76 108 Lab 10 1 Dna Structure And Replication The Chegg Com



9 2 Dna Replication Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition



Shetlerclass Files Wordpress Com 16 08 Worksheet Dna Structure And Replication Answer Key Pdf




Ward S Dna Structure And Replication Molecular Model Ward S Science




Structure And Diagrams Of Dna Replication Dna Replication Structure And Diagrams Dna Replication Structure And Diagrams 1 Dna Dna Replication Biology Lessons
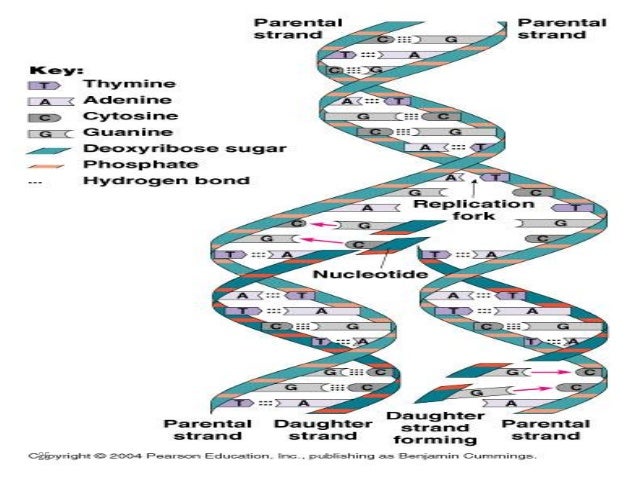



Lec 10 Level 3 De Dna Structure And Replication



Dna Structure And Replication Worksheet




Heredity Structure And Composition Of Dna Britannica




Dna Structure Dna Replication Biology Online Tutorial



9 2 Dna Replication Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition




Dna Replication Biology For Non Majors I



The Replication Of Dna




Lab Activity Dna Structure And Replication By The Skye World Science



Dna Structure Dna Replication Ms Tam S Website Biology Community Health Forensic Biology



Sweet Science Modeling Dna Replication Using Your Favorite Candies Small Online Class For Ages 11 16 Outschool




Dna Structure And Replication Diagram Quizlet




Dna Structure And Replication Practice 1 Pdf Dna Structure And Replication Practice Concept 10 Dna Structure And Replication Nucleotide 3 Directions Course Hero




Dna Structure And Replication Worksheet



4 3 Dna Structure And Replication Biology Libretexts



1



Dna Pogil Pdf Fill Online Printable Fillable Blank Pdffiller




Dna Structure And Replication




Dna Structure And Replication Crash Course Biology 10 Youtube



Modes Of Dna Replication



Dna Structure And Replication Flip Ebook Pages 1 5 Anyflip Anyflip




Dna Replication Wikipedia



4 3 Dna Structure And Replication Biology Libretexts



4 3 Dna Structure And Replication Biology Libretexts



Ppt Chapter 13 Dna Structure And Replication Powerpoint Presentation Id




5 Dna Structure And Replication Pogil Pdf Dna Structure And Replication How Is Genetic Information Stored And Copied Why Deoxyribonucleic Acid Or Dna Course Hero




Heredity Structure And Composition Of Dna Britannica



Exam 3 Chs 5 Dna Structure And Replication Machinery 16 The Molecular Basis Of Inheritance Flashcards Easy Notecards




Dna Structure And Replication Dna Structure And Replication How Is Genetic Information Stored And Copied Why Deoxyribonucleic Acid Or Dna Is The Course Hero



Ib Dna Structure Replication Review Key 2 6 2 7 7 1




Bioknowledgy 7 1 Dna Structure And Replication Ahl




Deoxyribonucleic Acid Dna Accessscience From Mcgraw Hill Education
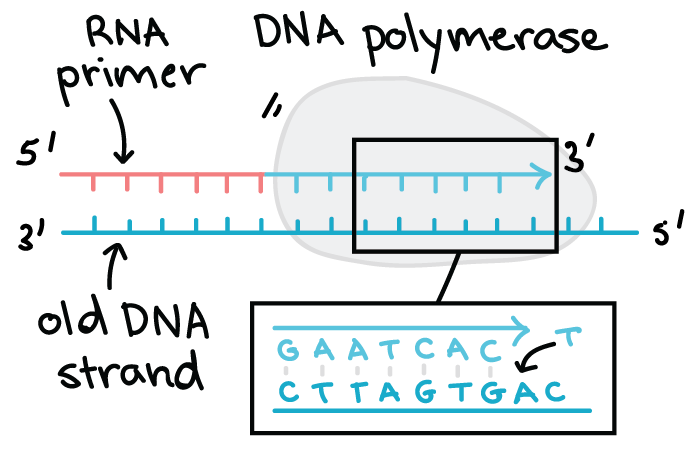



Dna Structure And Replication Review Article Khan Academy




Discovery Of Dna Double Helix Watson And Crick Learn Science At Scitable




Models Of Dna Structures Babyhabsbio11




Dna Replication Biol110summertest Confluence
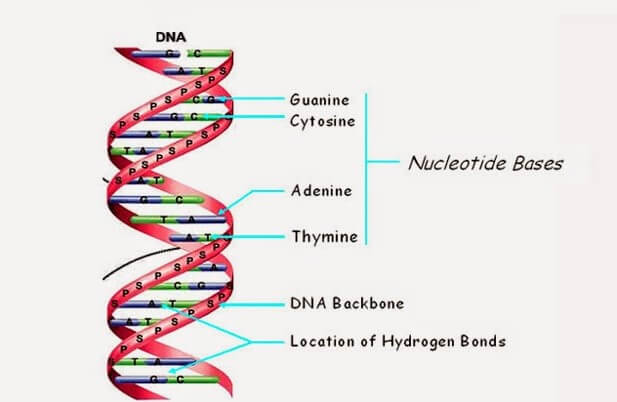



Dna Structure Watson And Crick S Model Of Dna Javatpoint



Modeling Dna Structure And Dna Replication Worksheet For 7th 9th Grade Lesson Planet
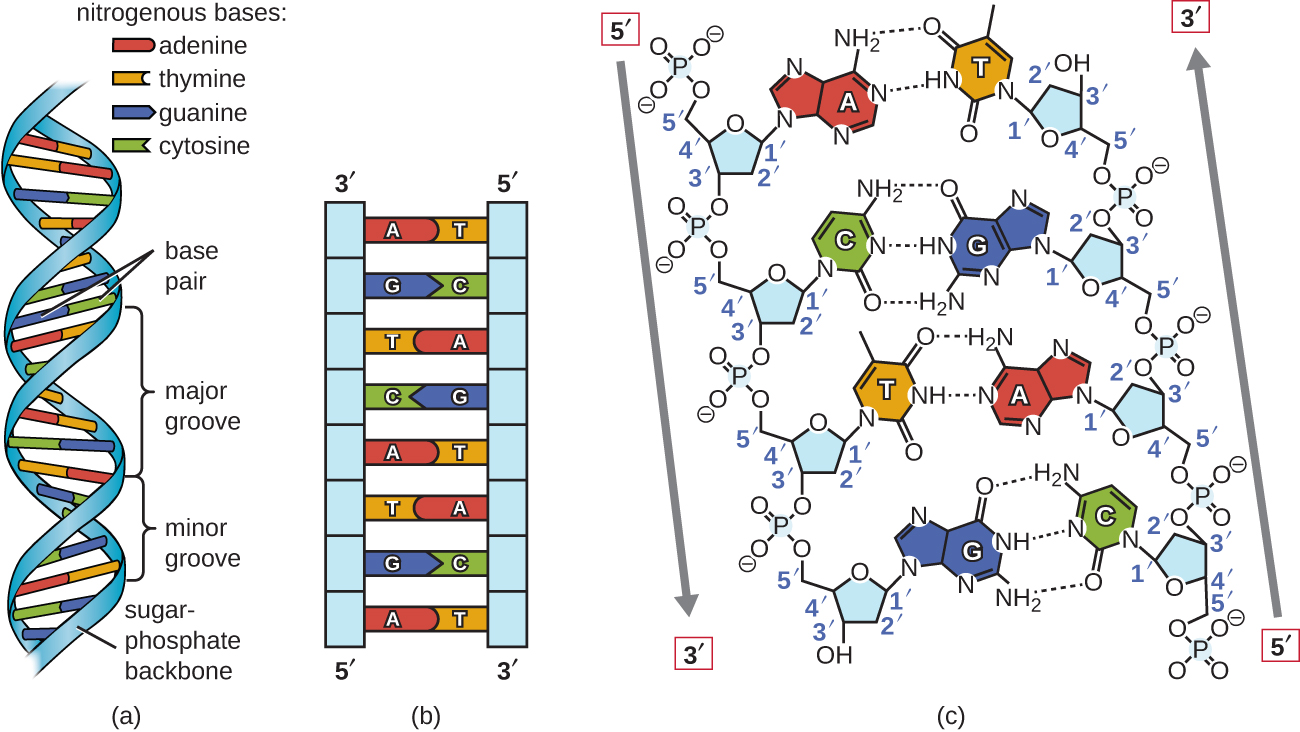



6 2 Structure And Replication Of Dna Biology Libretexts




Models Of Dna Structure Dna Model Project Dna Project Dna




Lesson 06 Dna Structure Dna Replication And Polymerase Chain Reaction Mariner Marine Genetics Lab
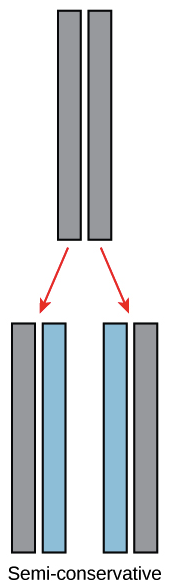



Dna Structure And Replication Review Article Khan Academy




The Structure Of Dna Genetics The Structure Of Dna




4 3 Dna Replication Dna Replication Watson And Cricks Model Of Dna Structure Suggested How Dna Could Replicate Hydrogen Bonds Break Helix Unzip Course Hero




Dna Synthesis Wikipedia
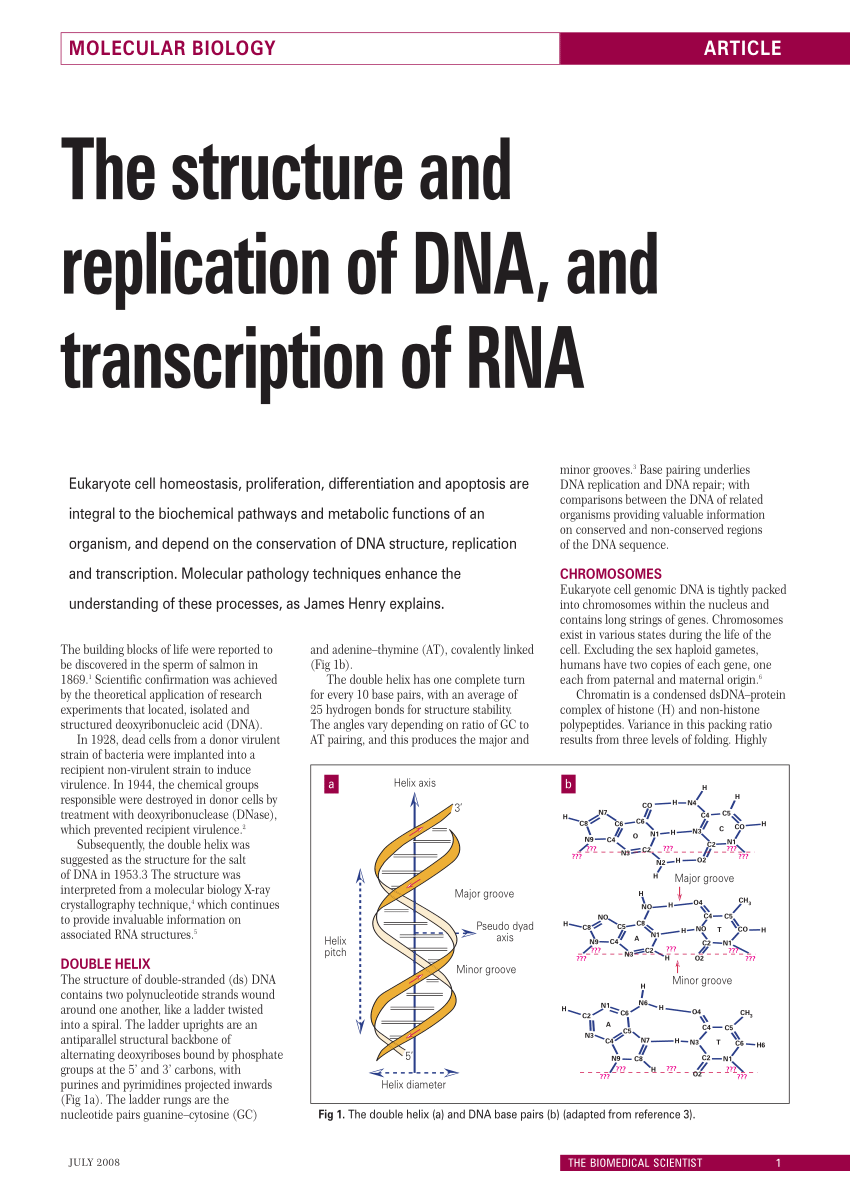



Pdf The Structure And Replication Of Dna And Transcription Of Rna A Modern Day Look



Dna Structure And Replication Hl Biology 16




Discovery Of Dna Double Helix Watson And Crick Learn Science At Scitable
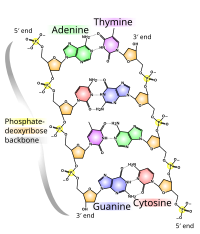



Molecular Models Of Dna Wikipedia




Heredity Structure And Composition Of Dna Britannica




Diagram Introduction Genetics Labeling The Diagrams Answer Key Full Version Hd Quality Answer Key Thadiagram Assimss It



Davison Dna Structure And Replication



コメント
コメントを投稿